Tuesday, June 28, 2011
WebSim( MIT open course Electronics Lab)
This is very interesting to do the basic electronics lab through the MIT open Electronics Lab (Web Sim) , also can listen excellent lectures from MIT professor on Basic Electronics
Wednesday, March 2, 2011
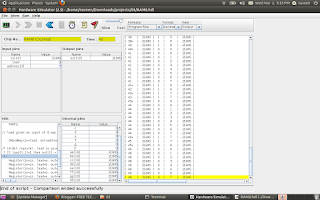
RAM8
RAM8:is a memory unit of 8 registers joined together to store 16*8 bits (16 byte). Based on the address (3bits) ,the Dmux8way device control the load signal for each Registers.
CHIP RAM8 {
IN in[16], load, address[3];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
// load given as input of 8 way Demultipelxer so that 'load' is seperated to control each Registers
DMux8Way(in=load, sel=address, a=a, b=b, c=c, d=d, e=e, f=f, g=g, h=h);
/* 16-Bit register, load is given as each seperated lines
* If load[t-1]=1 then out[t] = in[t-1]
*/
Register(in=in, load=a, out=aa);
Register(in=in, load=b, out=bb);
Register(in=in, load=c, out=cc);
Register(in=in, load=d, out=dd);
Register(in=in, load=e, out=ee);
Register(in=in, load=f, out=ff);
Register(in=in, load=g, out=gg);
Register(in=in, load=h, out=hh);
// 16bit outputs from each Registers connected through 16bit 8 way multiplexer in order to get the outputs based on the Address
Mux8Way16(a=aa, b=bb, c=cc, d=dd, e=ee, f=ff, g=gg, h=hh, sel=address, out=out);
}
CHIP RAM8 {
IN in[16], load, address[3];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
// load given as input of 8 way Demultipelxer so that 'load' is seperated to control each Registers
DMux8Way(in=load, sel=address, a=a, b=b, c=c, d=d, e=e, f=f, g=g, h=h);
/* 16-Bit register, load is given as each seperated lines
* If load[t-1]=1 then out[t] = in[t-1]
*/
Register(in=in, load=a, out=aa);
Register(in=in, load=b, out=bb);
Register(in=in, load=c, out=cc);
Register(in=in, load=d, out=dd);
Register(in=in, load=e, out=ee);
Register(in=in, load=f, out=ff);
Register(in=in, load=g, out=gg);
Register(in=in, load=h, out=hh);
// 16bit outputs from each Registers connected through 16bit 8 way multiplexer in order to get the outputs based on the Address
Mux8Way16(a=aa, b=bb, c=cc, d=dd, e=ee, f=ff, g=gg, h=hh, sel=address, out=out);
}

Tuesday, February 8, 2011
How to build a Memory for a computing System
BIT STORE
The elementary functionality of a Computing System is that it should store data somewhere and should be collected it back whenever require. We can call this block as Memory unit of a computer. The Memory can be build using the sequential chip called flip-flop. Below HDL can store a bit . The small memory can Write and Read using the 'load' signal.
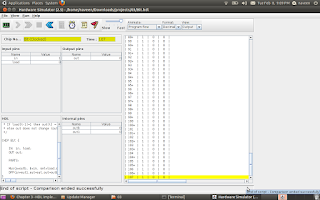
CHIP Bit {
IN in, load;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Mux(a=outb, b=in, sel=load,out=out1); //Mux input taken as the feedback of D-Flip Flop out
DFF(in=out1,out=out,out=outb);
}
================================================================================
Register
If a Bus(16bit) connected to 16 parallel a Bit chip ,then we can store 16bit at a time. This is known as Register.
CHIP Register {
IN in[16], load;
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
Bit(in=in[0],load=load,out=out[0]);
Bit(in=in[1],load=load,out=out[1]);
Bit(in=in[2],load=load,out=out[2]);
Bit(in=in[3],load=load,out=out[3]);
Bit(in=in[4],load=load,out=out[4]);
Bit(in=in[5],load=load,out=out[5]);
Bit(in=in[6],load=load,out=out[6]);
Bit(in=in[7],load=load,out=out[7]);
Bit(in=in[8],load=load,out=out[8]);
Bit(in=in[9],load=load,out=out[9]);
Bit(in=in[10],load=load,out=out[10]);
Bit(in=in[11],load=load,out=out[11]);
Bit(in=in[12],load=load,out=out[12]);
Bit(in=in[13],load=load,out=out[13]);
Bit(in=in[14],load=load,out=out[14]);
Bit(in=in[15],load=load,out=out[15]);
}
The elementary functionality of a Computing System is that it should store data somewhere and should be collected it back whenever require. We can call this block as Memory unit of a computer. The Memory can be build using the sequential chip called flip-flop. Below HDL can store a bit . The small memory can Write and Read using the 'load' signal.

CHIP Bit {
IN in, load;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Mux(a=outb, b=in, sel=load,out=out1); //Mux input taken as the feedback of D-Flip Flop out
DFF(in=out1,out=out,out=outb);
}
================================================================================
Register
If a Bus(16bit) connected to 16 parallel a Bit chip ,then we can store 16bit at a time. This is known as Register.
CHIP Register {
IN in[16], load;
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
Bit(in=in[0],load=load,out=out[0]);
Bit(in=in[1],load=load,out=out[1]);
Bit(in=in[2],load=load,out=out[2]);
Bit(in=in[3],load=load,out=out[3]);
Bit(in=in[4],load=load,out=out[4]);
Bit(in=in[5],load=load,out=out[5]);
Bit(in=in[6],load=load,out=out[6]);
Bit(in=in[7],load=load,out=out[7]);
Bit(in=in[8],load=load,out=out[8]);
Bit(in=in[9],load=load,out=out[9]);
Bit(in=in[10],load=load,out=out[10]);
Bit(in=in[11],load=load,out=out[11]);
Bit(in=in[12],load=load,out=out[12]);
Bit(in=in[13],load=load,out=out[13]);
Bit(in=in[14],load=load,out=out[14]);
Bit(in=in[15],load=load,out=out[15]);
}